What are the top trading blocs in the world?
Explore the top trading blocs worldwide, such as the APEC, European Union, NAFTA, ASEAN, Mercosur, and BRICS. Learn and get comprehensive details on how these alliances impact global trade and foster economic integration.

Trade blocs or trading blocs, also known as economic blocs, play a vital part in global trade. These indigenous agreements between countries aim to boost profitable cooperation and ease the inflow of goods, services, and investments across borders. In this article, we will explore the top trading blocs in the world, their advantages and disadvantages, and the significant part they play in shaping global frugality.
What are Trade Blocs?
A trade bloc refers to a group of countries that come together to form a profitable alliance, primarily aimed at reducing walls to trade within their region. These blocs operate on the principle of preferential trading arrangements, granting member nations favorable treatment over non-members when it comes to tariff rates, share allocations, and nonsupervisory fabrics. Trading blocs are indigenous profitable agreements between countries that promote trade and profitable integration. These blocs generally exclude or reduce trade walls, similar as tariffs and proportions, among member nations. The main ideal of trade blocs is to enhance profitable cooperation, produce a larger request, and stimulate investments within the sharing countries.
What are the different types of Trading Blocs?
Trading Blocs can take various forms and have different parts of integration. Some major types of Trading Blocs include:
- Preferential trading areas
The most abecedarian type of trading blocs are preferential trading areas, or PTAs. These agreements are comparatively adaptable. Trade restrictions, similar as tariffs and proportions, are lessened in preferential trading areas (PTAs) for some but not all goods changed between member nations. India and Chile are party to a PTA. As a result, trade walls are lower, and 1800 goods can be traded between the two nations.
- Free trade areas
Agreements known as free trade areas (FTAs) exclude all limitations or trade walls among the sharing nations. Every member is still free to choose how to handle trade with non-member nations or groups (those not included in the agreement). One illustration of an FTA is the United States, Mexico, and Canada Agreement, or USMCA. Every nation has the freedom to trade with every other nation including with nations that aren't parties to this agreement.
- Customs unions
Custom unions are agreements made by trading blocs or nations. In addition to agreeing to lift trade walls between one another, members of a customs union also commit to administering the same import restrictions on non-member nations. There's a customs union agreement between the European Union (EU) and Turkey. Turkey has the right to trade freely with any member of the EU, but it must put common external tariffs (CETs) on non-EU nations.
- Common markets
The accords governing the customs union are expanded upon by the common request. The elimination of trade restrictions and unrestricted labor and capital inflow among its actors define a common request. Occasionally, a" single request" is used to allude to a common request. One illustration of a participated or single request is the European Union (EU). All 27 nations freely and unrestrictedly enjoy trading with one another. The free inflow of capital and labor is also present.
- Economic unions
Another name for a profitable union is a" financial union," and it's basically an expansion of a participated market. Barring trade restrictions, allowing traders and labor to flow freely, and unifying their husbandry under a common currency are the emblems of a profitable union. One EU member that has embraced the euro is Germany. Trade between Germany and other EU nations who have accepted the euro, like Portugal, and those that haven't, like Denmark, is unrestricted.
Top 10 Trade Blocs in the world
The top 10 global trade blocs in 2022-23 are mentioned in the list below:
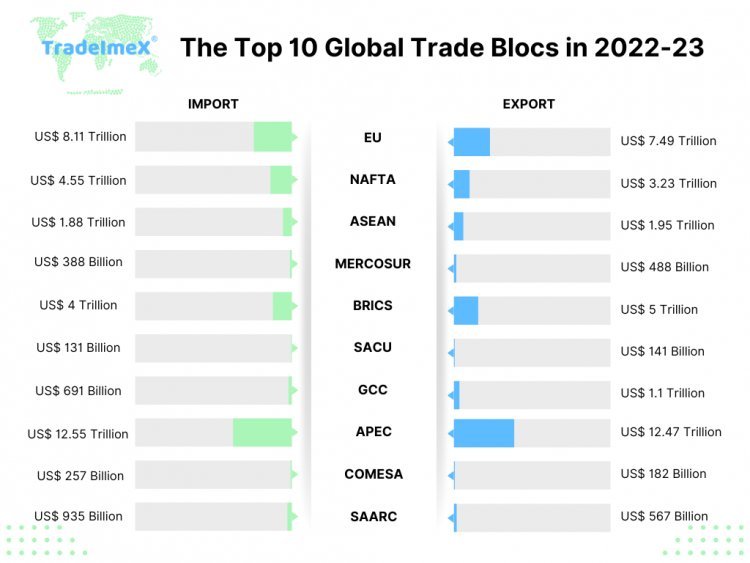
- APEC (exports: $12.47 trillion, imports: $12.55 trillion)
- EU (exports: $7.49 trillion, imports: $8.11 trillion)
- BRICS (exports: $5 trillion, imports: $4 trillion)
- NAFTA (exports: $3.23 trillion, imports: $4.55 trillion)
- ASEAN (exports: $1.95 trillion, imports: $1.88 trillion)
- GCC (exports: $1.1 trillion, imports: $691 billion)
- SAARC (exports: $567 billion, imports: $935 billion)
- MERCOSUR (exports: $448 billion, imports: $388 billion)
- COMESA (exports: $182 billion, imports: $257 billion)
- SACU (exports: $141 billion, imports: $131 billion)
- Asia- Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
APEC is an association of 21 Pacific Rim members, promoting indigenous profitable integration and free trade. APEC also included member husbandry, which together accounts for around 60% of global GDP. It's in charge of promoting trade, investment, cooperation, and profitable progress in this area. The 21 nations that make up APEC are Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Chile, China, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Mexico, Malaysia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Taipei, Thailand, United States, and Vietnam. In 2022, the total value of products exported by APEC was $12.47 trillion, while the total value of goods imported was $12.55 trillion. The two largest trade nations are the United States and China
- European Union (EU)
The EU is the largest trading bloc in the world, conforming of 27 member countries. It promotes the free movement of goods, services, capital, and people within its borders, creating a single request with over 446 million consumers. Innovated in 1951, the European Union is the world's most intertwined trade union. In addition to creating a single request for all of Europe, it also introduced the Euro as a single currency for intraregional trade. The European Union imported $8.11 trillion worth of goods and exported $7.49 trillion worth to the global request in 2022.
- BRICS
The five nations of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa are together appertained to as BRICS. nonetheless, South Africa only came a member of this group in 2010, when it was still appertained to as BRIC. In 2022, the combined value of BRICS exports and imports was $5 trillion and $4 trillion, independently. China reckoned for 14.6% of BRICS exports and 10.7% of BRICS imports, making it the largest trading nation among these nations in terms of both imports and exports.
- North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
NAFTA, now replaced by the United States- Mexico- Canada Agreement (USMCA), aimed to exclude trade walls between the United States, Canada, and Mexico. This bloc facilitates trade among its member nations in colorful sectors. In 2022, NAFTA goods imports totaled $4.55 trillion, while exports totaled $3.23 trillion. Among the NAFTA nations, the United States is the most trading nation.
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
ASEAN is an indigenous association conforming of ten Southeast Asian countries. It promotes profitable integration and cooperation among member nations, leading to increased trade and investments in the region. ASEAN was innovated in Bangkok, Thailand, on August 8, 1967. Brunei, Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Indonesia, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, Philippines, and Myanmar are among the ten nations that make up ASEAN. adding profitable growth, advancing social progress, and fostering indigenous stability and space are the core objects of ASEAN. Its thing is to unite ASEAN into one region. The largest trading request among ASEAN nations is Singapore. The trade data indicates that in 2022, ASEAN imported $1.88 trillion worth of goods and exported $1.95 trillion worth of goods to the world request.
- Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
The GCC comprises six Arab nations in the Persian Gulf region. It fosters profitable cooperation, including the free movement of goods, services, and investments, among its member countries. The GCC, known as the" profitable hustler of the Middle East," has seen a significant increase in global trade over time. 2022 has been no different, with the region's trade volume expanding across a number of sectors. The total value of imported goods by the GCC in 2022 was $691 billion, while the total exported goods valued worth $1.1 trillion.
- (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) SAARC
SAARC, which stands for South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, is a famed trade bloc comprising eight countries in South Asia. With its commencement in 1985, SAARC has played a vital part in promoting profitable cooperation, indigenous integration, and political stability in the region. SAARC nations include Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Maldives, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. It was established on the 8th of December 1985. In 2022, SAARC's global goods exports were valued at $567 billion, while its global imports were valued at $935 billion. Among SAARC nations, India is the biggest trading mate in terms of both imports and exports.
- Mercosur (Southern Common Market)
The Southern Common Market, also known as MERCOSUR, was created on March 26, 1991. South American countries that cover the requests of Brazil, Argentina, Venezuela, Paraguay, and Uruguay have formed a tariff union. Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, and Ecuador are among its associate members. Its primary objective is to quicken the pace of steady profitable growth. One of the trading blocs with the quickest rate of growth in the world is MERCOSUR. The two most common languages spoken in this area are Portuguese and Spanish. It aims to promote free trade and profitable development among its member nations. Its exports are valued at $448 billion, while imports at $388 billion in 2022.
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
COMESA is an indigenous profitable community conforming of 21 African nations. It aims to produce a common trade market and grease profitable integration within the Eastern and Southern African region. A group of independent, autonomous nations that have come together to support the growth of indigenous or transnational trade is known as COMESA. It's a profitable union of nations in eastern and southern Africa. Burundi, Comoros, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Rwanda, Seychelles, Sudan, Swaziland, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe are among its 19 member nations. In 2022, COMESA imports total $257 billion and exports total $182 billion. Out of all the COMESA nations, Egypt is the biggest dealer.
- Southern African Customs Union (SACU)
SACU consists of South Africa, Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, and Namibia. This customs union aims to grease indigenous integration, enhance artificial development, and promote profitable cooperation in Southern Africa. In 2022, SACU exports made up 24% of all South African exports, valued at over$ 141 billion. About $131 billion worth of SACU imports were made in 2022; this amounted to just 9% of all imports into the nation.
What is the role of trading blocs?
Trading blocs play a significant part in shaping global frugality. They grease indigenous integration, enhance trade volumes, stimulate profitable growth, and promote political cooperation among member countries. Also, they enable the adjustment of regulations, norms, and programs, creating a position playing field for businesses operating within the bloc.
Advantages of trade blocs
- Increased market access: One of the significant advantages of trade blocs is increased market access for member countries. By barring trade walls, similar as tariffs and proportions, member nations have easier access to each other's requests, leading to expanded trade volumes and openings for businesses.
- Husbandry of scale: Trade blocs allow member countries to achieve husbandry of scale by pooling coffers and participating product capabilities. This results in lower product costs, increased effectiveness, and the capability to contend encyclopedically on a larger scale.
- Enhanced political cooperation: Trade blocs frequently go beyond profitable integration and foster political cooperation among member nations. This collaboration promotes stability, peace, and politic ties between countries.
- Specialization and relative advantage: Trade blocs allow member countries to specialize in producing goods and services in which they've a relative advantage. This leads to increased effectiveness and productivity, serving all sharing nations.
Disadvantages of trade blocs
- Trade diversion: While trade blocs can boost indigenous trade, they may also divert trade down from non-member countries. This could lead to profitable losses for nations outside the bloc, especially if they preliminarily had significant trading connections with member countries.
- Loss of sovereignty: Joining a trade bloc may affect a loss of profitable sovereignty for member countries. They need to cleave to the regulations and programs set by the bloc, limiting their capability to singly formulate trade programs and negotiate agreements with non-member countries.
- Complex accommodations: Negotiating trade agreements within a bloc involves complex and time- consuming conversations between member countries. dissensions on different issues, similar as tariffs, intellectual property rights, and disagreement agreement mechanisms, can further complicate accommodations.
- Inequality among member states: Trade blocs may exacerbate existing inequalities among member countries. Developed nations within the bloc often have a competitive advantage over smaller or less developed economies, leading to unequal distribution of benefits and potential negative impacts on less developed nations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, trading blocs or economic blocs continue to shape the global trade geography, promoting profitable cooperation and integration among member countries. While they offer multitudinous advantages, including increased request access and husbandry of scale, they also face challenges similar as trade diversion and loss of sovereignty. Understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and part of trading blocs is essential for governments, businesses, and individuals navigating the complications of global frugality.
Read More:-
Medical Equipment Exports in 2022
What's Your Reaction?














